
 Tutorials Tutorials | (back to the list of tutorials) |
 Panelization Example6
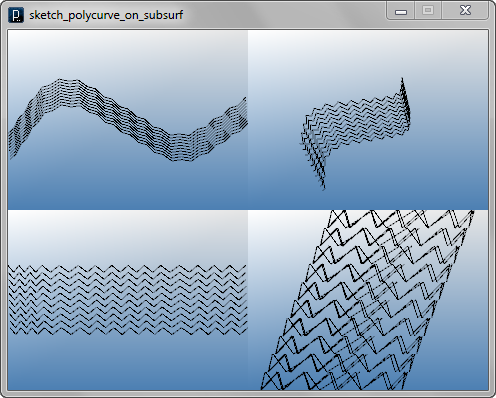
Panelization Example6![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
import processing.opengl.*;
import igeo.*;
size(480, 360, IG.GL);
IG.open("surface8.3dm");
ISurface[] surfaces = IG.surfaces();
int unum = 10, vnum = 30;
double uinc = 1.0/unum, vinc = 1.0/vnum;
for (ISurface surf : surfaces) {
for (int i=0; i < unum; i++) {
IVec[] pts = new IVec[vnum+1];
for (int j=0; j <= vnum; j++) {
if (j%2==0) {
pts[j] = surf.pt(i*uinc, j*vinc);
}
else {
pts[j] = surf.pt((i+1)*uinc, j*vinc);
}
}
new ICurve(pts).clr(0);
}
surf.del();
}
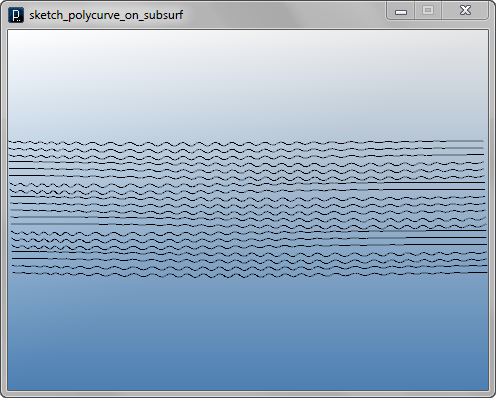
 Then amount of undulation is controlled by image mapping.
The degree of the curve is also changed to create curvature.
The input bitmap used in the example is this.
Then amount of undulation is controlled by image mapping.
The degree of the curve is also changed to create curvature.
The input bitmap used in the example is this.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
import processing.opengl.*;
import igeo.*;
size(480, 360, IG.GL);
IG.open("surface8.3dm");
ISurface[] surfaces = IG.surfaces();
int unum = 20, vnum = 60;
double uinc = 1.0/unum, vinc = 1.0/vnum;
IImageMap map = new IImageMap("map3.jpg");
for (ISurface surf : surfaces) {
for (int i=0; i < unum; i++) {
IVec[] pts = new IVec[vnum+1];
for (int j=0; j <= vnum; j++) {
if (j%2==0) {
pts[j] = surf.pt(i*uinc, j*vinc);
}
else {
// bitmap value is sampled. note that u and v is swapped to match with u-v of the input surface.
double val = map.get( j*vinc, i*uinc );
pts[j] = surf.pt((i+val)*uinc, j*vinc);
}
}
new ICurve(pts, 2).clr(0);
}
surf.del();
}
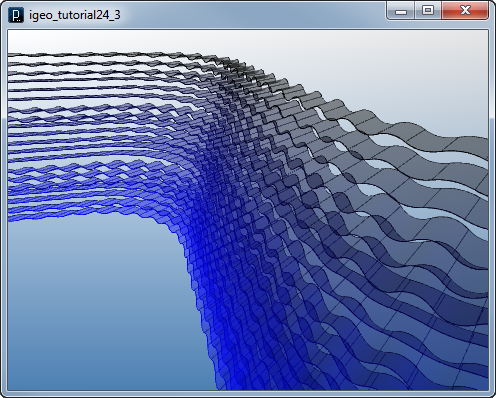
Then the curves are extruded in the y-axis direction.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
import processing.opengl.*;
import igeo.*;
size(480, 360, IG.GL);
IG.open("surface8.3dm");
ISurface[] surfaces = IG.surfaces();
int unum = 20, vnum = 60;
double uinc = 1.0/unum, vinc = 1.0/vnum;
IImageMap map = new IImageMap("map3.jpg");
for (ISurface surf : surfaces) {
for (int i=0; i < unum; i++) {
IVec[] pts = new IVec[vnum+1];
for (int j=0; j <= vnum; j++) {
if (j%2==0) {
pts[j] = surf.pt(i*uinc, j*vinc);
}
else {
// bitmap value is sampled. note that u and v is swapped to match with u-v of the input surface.
double val = map.get( j*vinc, i*uinc );
pts[j] = surf.pt((i+val)*uinc, j*vinc);
}
}
ICurve crv = new ICurve(pts, 2).clr(0);
IVec extrudeDir = new IVec(0, -2, 0);
IG.extrude(crv, extrudeDir).clr(0,0,i*uinc,0.5);
}
surf.del();
}
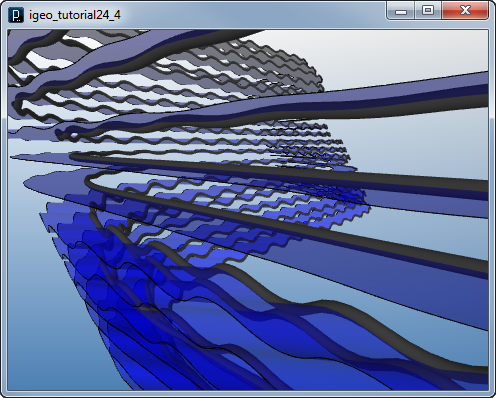
Then the depth of extrusion is randomized and pipe geometry is added on the edge of the extruded surface.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
import processing.opengl.*;
import igeo.*;
size(480, 360, IG.GL);
IG.open("surface8.3dm");
ISurface[] surfaces = IG.surfaces();
int unum = 20, vnum = 60;
double uinc = 1.0/unum, vinc = 1.0/vnum;
IImageMap map = new IImageMap("map3.jpg");
for (ISurface surf : surfaces) {
for (int i=0; i < unum; i++) {
IVec[] pts = new IVec[vnum+1];
for (int j=0; j <= vnum; j++) {
if (j%2==0) {
pts[j] = surf.pt(i*uinc, j*vinc);
}
else {
// bitmap value is sampled. note that u and v is swapped to match with u-v of the input surface.
double val = map.get( j*vinc, i*uinc );
pts[j] = surf.pt((i+val)*uinc, j*vinc);
}
}
ICurve crv = new ICurve(pts, 2).clr(0);
IVec extrudeDir = new IVec(0, IRandom.get(-3, -1), 0);
IG.extrude(crv, extrudeDir).clr(0,0,i*uinc,0.5);
ICurve crv2 = crv.cp(extrudeDir);
IG.pipe(crv2, 0.1).clr(0.2);
}
surf.del();
}
 HOME
HOME
 FOR PROCESSING
FOR PROCESSING
 DOWNLOAD
DOWNLOAD
 DOCUMENTS
DOCUMENTS
 TUTORIALS (Java /
Python)
TUTORIALS (Java /
Python)
 GALLERY
GALLERY
 SOURCE CODE(GitHub)
SOURCE CODE(GitHub)
 PRIVACY POLICY
PRIVACY POLICY
 ABOUT/CONTACT
ABOUT/CONTACT
