
 Python Tutorials Python Tutorials | (back to the list of tutorials) |
 Define Interact Method
Define Interact MethodThe below is a template to define an interact method.
![]()
![]()
![]()
add_library('igeo')
def setup() :
size(480, 360, IG.GL)
agent = MyAgent()
class MyAgent(IAgent) :
def interact(self, agents) :
# definition of interact behavior
def update(self) :
# definition of update behavior
You can write any code you want inside interact method to define the behavior of interaction but most of the time when you have only one agent class to interact, the code would look like the following template to have for-loop iteration to check all other agents.
![]()
![]()
![]()
add_library('igeo')
def setup() :
size(480, 360, IG.GL)
agent = MyAgent()
class MyAgent(IAgent) :
def interact(self, agents) :
for agent in agents : #check all existing agents
if isinstance(agent, MyAgent) : #type check
if agent is not self : #agents include this instance itself
# definition of interact behavior
def update(self) :
# definition of update behavior
The interact method starts with the line
This for-loop on the first line is to iterate
through all the existing agents in side the agents
variable.
In the for-loop, the number is counted up to agents.size(),
which is total number of member inside the variable array.
for(int i=0; i < agents.size(); i++){
This if-condition on the second line is to check if the variable inside the variable-length array agents is an instance of MyAgent. agents.get(i) is to access the i-th member inside the array. The keyword "instanceof" is to check if the variable is an instance of the class MyAgent because the input argument agents could contain any type of agents.
if(agents.get(i) instanceof MyAgent){
The third line is to "cast" the variable of an unknown class into a variable of MyAgent class. The "casting" is a process to convert an instance of a superclass into that of subclass. Casting can be done by putting "(" + name of class + ")" in front of the variable. For more description about casting, please see this Java tutorial.
MyAgent agent = (MyAgent)agents.get(i);
Then on the fourth line it exclude the case the variable contained inside the variable-length array agents is the same instance with the one which is checking others right now. "this" refers to the currently executing instance itself.
if(agent!= this){
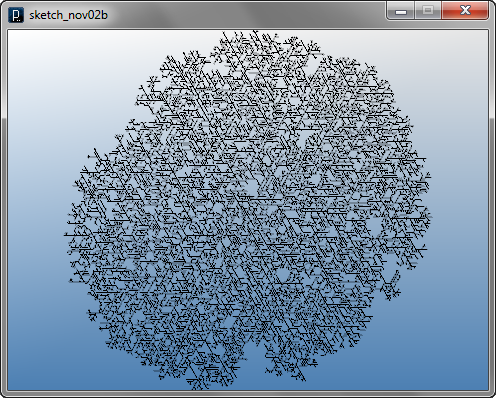
 Interact Method Example 1
Interact Method Example 1
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
add_library('igeo')
def setup() :
size(480, 360, IG.GL)
IG.duration(120)
agent = LineAgent(IVec(0,0,0), IVec(1,0,0))
class LineAgent(IAgent) :
length = 2
clearance = 1.99 #less than length
def __init__(self, pt, dir) :
self.pt1 = pt
self.pt2 = pt.dup().add(dir.dup().len(LineAgent.length))
self.isColliding = False
def interact(self, agents) :
if self.time() == 0 : #only in the first time
for agent in agents :
if isinstance(agent, LineAgent) :
if agent is not self :
# checking clearance of end point
if agent.pt2.dist(self.pt2) < LineAgent.clearance :
self.isColliding=True
def update(self) :
if self.isColliding :
self.del()
elif self.time() == 0 : #if not colliding
ICurve(self.pt1, self.pt2).clr(0)
dir = self.pt2.dif(self.pt1)
if IRand.pct(40) : #bend
LineAgent(self.pt2, dir.dup().rot(PI/3))
if IRand.pct(40) : #bend the other way
LineAgent(self.pt2, dir.dup().rot(-PI/3))
if IRand.pct(80) : #straight
LineAgent(self.pt2, dir.dup())
In this algorithm, the interact method is checking collision with any existing LineAgent by this if-condition.
if(lineAgent.pt2.dist(pt2) < clearance){
In the update method, if it finds any collision, i.e. the variable isColliding is true, it delete itself and doesn't create a line. Otherwise, it puts a line and creates 3 child agents randomly in the direction of 60 degrees (PI/3), -60 degrees and straight. This inteaction and update logics are described in the following diagram.
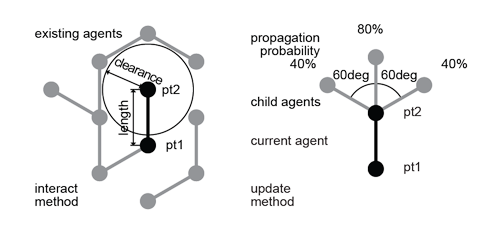
All of this collision check and geometry and child agents generation is only done once at the time frame of 0 by the if-condition "if(time == 0){" which appears on both of interact and update method. The variable "time" is an instance field of IAgent showing how many updating cycles have elapsed since the instance is created.
The below shows the same algorithm written with the longer definition of the interact method in case the speed of the execution matters.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
add_library('igeo')
def setup() :
size(480, 360, IG.GL)
IG.duration(120)
agent = LineAgent(IVec(0,0,0), IVec(1,0,0))
class LineAgent(IAgent) :
length = 2
clearance = 1.99 #less than length
def __init__(self, pt, dir) :
self.pt1 = pt
self.pt2 = pt.dup().add(dir.dup().len(LineAgent.length))
self.isColliding = False
def interact(self, agents) :
if self.time() == 0 : #only in the first time
for agent in agents :
if isinstance(agent, LineAgent) :
if agent is not self :
# checking clearance of end point
if agent.pt2.dist(self.pt2) < LineAgent.clearance :
self.isColliding=True
def update(self) :
if self.isColliding :
self.del()
elif self.time() == 0 : #if not colliding
ICurve(self.pt1, self.pt2).clr(0)
dir = self.pt2.dif(self.pt1)
if IRand.pct(40) : #bend
LineAgent(self.pt2, dir.dup().rot(PI/3))
if IRand.pct(40) : #bend the other way
LineAgent(self.pt2, dir.dup().rot(-PI/3))
if IRand.pct(80) : #straight
LineAgent(self.pt2, dir.dup())
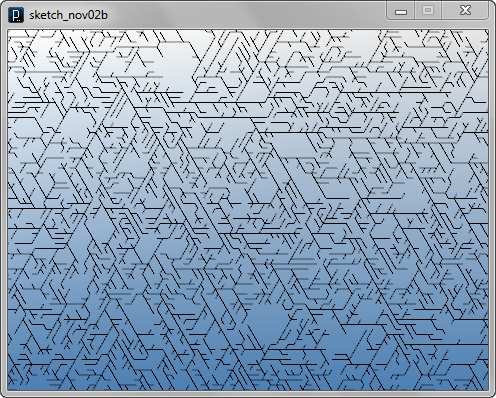
 Interact Method Example 2
Interact Method Example 2Please note that the range of random angle of branching is from PI/3 to PI/3*2 because if the angle is less than PI/3, the end point would collide with straight member. Or if the angle is more than PI/3*2, it would collide with the parent line when you have LineAgent.length and LineAgent.clearance close. LineAgent.clearance cannot be larger than LineAgent.length because an agent would judge that the line always collides with the parent line.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
add_library('igeo')
def setup() :
size(480, 360, IG.GL)
IG.duration(250)
agent = LineAgent(IVec(0,0,0), IVec(1,0,0))
class LineAgent(IAgent) :
length = 2
clearance = 1.99 #less than length
def __init__(self, pt, dir) :
self.pt1 = pt
self.pt2 = pt.dup().add(dir.dup().len(LineAgent.length))
self.isColliding = False
def interact(self, agents) :
if self.time() == 0 : #only in the first time
for agent in agents :
if isinstance(agent, LineAgent) :
if agent is not self :
# checking clearance of end point
if agent.pt2.dist(self.pt2) < LineAgent.clearance :
self.isColliding=True
def update(self) :
if self.isColliding :
self.del()
elif self.time() == 0 : #if not colliding
ICurve(self.pt1, self.pt2).clr(0)
dir = self.pt2.dif(self.pt1)
if IRand.pct(40) : #bend
LineAgent(self.pt2, dir.dup().rot(IRand.get(PI/3,PI/3*2)))
if IRand.pct(40) : #bend the other way
LineAgent(self.pt2, dir.dup().rot(-IRand.get(PI/3,PI/3*2)))
if IRand.pct(80) : #straight
LineAgent(self.pt2, dir.dup())
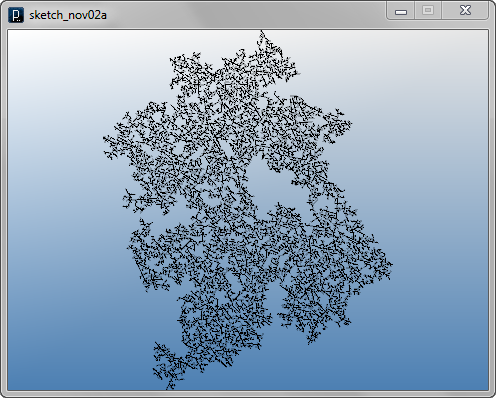
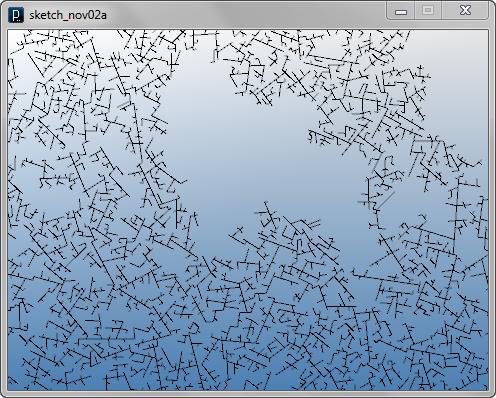
 Interact Method Example 3
Interact Method Example 3![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
add_library('igeo')
def setup() :
size(480, 360, IG.GL)
IG.duration(150)
agent = LineAgent(IVec(0,0,0), IVec(1,0,0))
class LineAgent(IAgent) :
length = 2
clearance = 1.99 #less than length
def __init__(self, pt, dir) :
self.pt1 = pt
self.pt2 = pt.dup().add(dir.dup().len(LineAgent.length))
self.isColliding = False
def interact(self, agents) :
if self.time() == 0 : #only in the first time
for agent in agents :
if isinstance(agent, LineAgent) :
if agent is not self :
# checking clearance of end point
if agent.pt2.dist(self.pt2) < LineAgent.clearance :
self.isColliding=True
def update(self) :
if self.isColliding :
self.del()
elif self.time() == 0 : #if not colliding
ICurve(self.pt1, self.pt2).clr(0)
dir = self.pt2.dif(self.pt1)
#rotation axis with random direction
axis = IRand.pt(-1,1).len(1)
if IRand.pct(50) : #bend
LineAgent(self.pt2, dir.dup().rot(axis,IRand.get(PI/3,PI/3*2)))
if IRand.pct(50) : #bend the other way
LineAgent(self.pt2, dir.dup().rot(axis,-IRand.get(PI/3,PI/3*2)))
if IRand.pct(80) : #straight
LineAgent(self.pt2, dir.dup())
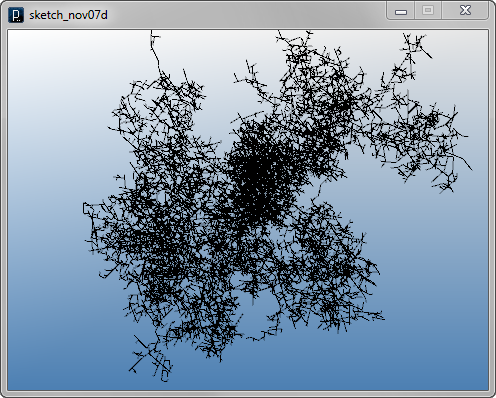
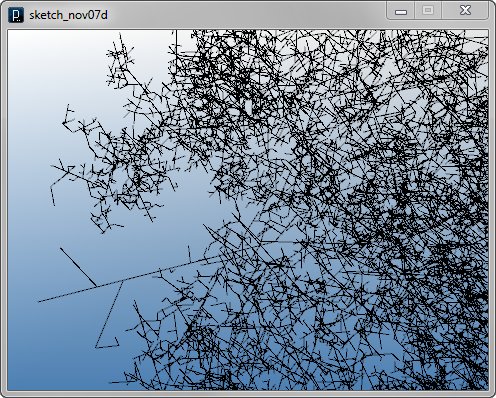
 Interact Method Example 4
Interact Method Example 4![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
add_library('igeo')
def setup() :
size(480,360,IG.GL)
IG.duration(400)
MySphereAgent(IRand.pt(-10,10),IRand.get(5,20))
MySphereAgent(IRand.pt(-10,10),IRand.get(5,20))
IG.fill()
class MySphereAgent(IAgent) :
def __init__(self, p, rad) :
self.pos = p
self.radius = rad
self.changed = True
self.sphere = None
def interact(self, agents) :
for agent in agents :
if isinstance(agent, MySphereAgent) :
if agent is not self :
dist = agent.pos.dist(self.pos)
if dist < self.radius + agent.radius :
dif = self.pos.dif(agent.pos)
#amount of overlap is this radius plus other radius minus distance between two centers
dif.len(self.radius+agent.radius-dist)
self.pos.add(dif) #only this agent is moved, not others
self.changed=True #state variable is updated
def update(self) :
if self.changed :
# update sphere
if self.sphere is not None :
self.sphere.del() #shpere is null first
self.sphere = ISphere(self.pos, self.radius).clr(self.clr())
self.changed=False
if self.time() == 5 : #delayed to create the next agent til time==5
# next agent's direction
dir = IRand.pt(-1, 1)
nextRadius = IRand.get(5, 20)
# amount of move is the current radius + the next one
dir.len(self.radius+nextRadius)
MySphereAgent(self.pos.cp(dir),nextRadius).clr(IRandom.clr())
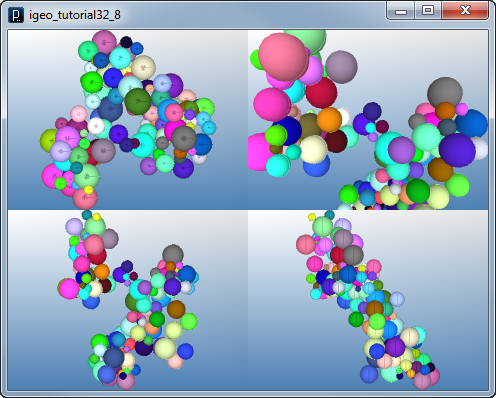
 Interact Method Example 5
Interact Method Example 5![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
add_library('igeo')
def setup() :
size(480, 360, IG.GL)
IConfig.syncDrawAndDynamics = True #for errors by heavier dynamics than drawing
IG.duration(500)
num=20
for i in range(num) :
RectAgent(IRand.pt(-100,-100,0,100,100, 0),20,20).clr(IRand.clr())
class RectAgent(IAgent) :
gap = 1.0
minSize = 1.0
maxSize = 20.0
def __init__(self, pt, w, h) :
self.pos = pt
self.width = w
self.height = h
self.anyChange = True
self.rect = None
def interact(self, agents) :
for agent in agents :
# shrink the size when it collides with others.
if isinstance(agent, RectAgent) :
if agent is not self :
# is it overlapping?
if agent.pos.x()+agent.width+RectAgent.gap > self.pos.x() and \
agent.pos.x() < self.pos.x()+self.width+RectAgent.gap and \
agent.pos.y()+agent.height+RectAgent.gap > self.pos.y() and \
agent.pos.y() < self.pos.y()+self.height+RectAgent.gap :
# both x and y overlapping?
if agent.pos.x() >= self.pos.x() and agent.pos.y() >= self.pos.y() :
if agent.pos.x() - self.pos.x() > agent.pos.y() - self.pos.y() :
self.width = agent.pos.x() - self.pos.x() - RectAgent.gap
else :
self.height = agent.pos.y() - self.pos.y() - agent.gap
self.anyChange = True
# x is right of pos
elif agent.pos.x() > self.pos.x() :
self.width = agent.pos.x() - self.pos.x() - RectAgent.gap
self.anyChange = True
# y is top of pos
elif agent.pos.y() > self.pos.y() :
self.height = agent.pos.y() - self.pos.y() - RectAgent.gap
self.anyChange = True
def update(self) :
# update geometry only when the size changes
if self.anyChange :
if self.rect is not None :
self.rect.del()
if self.width >= RectAgent.minSize and self.height >= RectAgent.minSize :
self.rect = IG.plane(self.pos, self.width, self.height).clr(self.clr())
# if too small, removed
else :
self.del()
self.anyChange=False
if self.time() == 0 :
RectAgent(self.pos.cp(IRand.pt(-10,-10, 0,10,10, 0)), \
IRand.get(RectAgent.minSize,RectAgent.maxSize), \
IRand.get(RectAgent.minSize,RectAgent.maxSize)).clr(self.clr())

 Interact Method Example 6
Interact Method Example 6![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
add_library('igeo')
def setup() :
size(480, 360, IG.GL)
IG.duration(100)
MyAutomaton(IVec(0, 0, 0))
class MyAutomaton(IAgent) :
size = 10
def __init__(self, p) :
self.pos = p
self.state = 1
self.leftAutomaton=None
self.rightAutomaton=None
self.lstate = 0
self.rstate = 0
def interact(self, agents) :
#searching left and right automaton
#if not found leftState & rightState are zero
for agent in agents :
if isinstance(agent, MyAutomaton) :
if agent is not self :
if agent.pos.eqX(self.pos.dup().sub(self.size,0,0)) :
self.leftAutomaton = agent
self.lstate = agent.state
elif agent.pos.eqX(self.pos.dup().add(self.size,0,0)) :
self.rightAutomaton = agent
self.rstate = agent.state
def update(self) :
# when state==1, put a box, otherwise no box
if self.state == 1 :
IBox(self.pos.dup(), self.size, self.size, self.size).clr(0)
# update state with a state transition table
if self.lstate==0 and self.state==0 and self.rstate==0 :
self.state = 0
elif self.lstate==0 and self.state==0 and self.rstate==1 :
self.state = 1
elif self.lstate==0 and self.state==1 and self.rstate==0 :
self.state = 1
elif self.lstate==0 and self.state==1 and self.rstate==1 :
self.state = 1
elif self.lstate==1 and self.state==0 and self.rstate==0 :
self.state = 1
elif self.lstate==1 and self.state==0 and self.rstate==1 :
self.state = 0
elif self.lstate==1 and self.state==1 and self.rstate==0 :
self.state = 0
elif self.lstate==1 and self.state==1 and self.rstate==1 :
self.state = 0
#move down
self.pos.add(0,-self.size,0)
#new automaton
if self.leftAutomaton is None :
MyAutomaton(self.pos.dup().sub(self.size,0,0))
if self.rightAutomaton is None :
MyAutomaton(self.pos.dup().add(self.size,0,0))
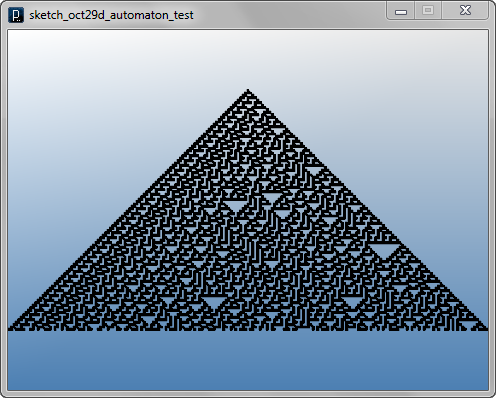

 Interact Method Example 7
Interact Method Example 7![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
add_library('igeo')
def setup() :
size(480, 360, IG.GL)
IG.duration(250)
LineAgent(IVec(0,0,0), IVec(0,1,0)).clr(0)
class LineAgent(IAgent) :
def __init__(self, pt, dir) :
self.pt1 = pt
self.pt2 = pt.cp(dir)
self.isColliding = False
def interact(self, agents) :
if self.time() == 0 : #only in the first time
for agent in agents :
if isinstance(agent, LineAgent) :
if agent is not self :
if not agent.isColliding and not self.isColliding :
intxn = IVec.intersectSegment(self.pt1,self.pt2,agent.pt1,agent.pt2)
if intxn is not None : #intersection exists
if not intxn.eq(self.pt1) : #not parent agent
self.isColliding = True
def update(self) :
if self.isColliding :
self.del()
elif self.time() == 0 : #if not colliding
ICurve(self.pt1,self.pt2).clr(self.clr())
dir = self.pt2.dif(self.pt1)
r = self.red()+IRand.get(0,0.01)
g = self.green()+IRand.get(0,0.01)
b = self.blue()+IRand.get(0,0.01)
if IRand.pct(40) : #bend
LineAgent(self.pt2, dir.dup().rot(IRand.get(0,PI/20))).clr(r,g,b)
if IRand.pct(40) : #bend the other way
LineAgent(self.pt2, dir.dup().rot(-IRand.get(0,PI/20))).clr(r,g,b)
if IRand.pct(40) : #straight
LineAgent(self.pt2, dir.dup()).clr(r,g,b)
An intersection of two line segments can be calculated by the following method.
IVec.intersectSegment(line1Pt1, line1Pt2, line2Pt1, line2Pt2);
If two line segments intersect, it returns one vector (IVec) as the location of intersection. If not, it returns a null value. Note that there is another intersect method for infinite lines.
IVec.intersect(line1Pt1, line1Pt2, line2Pt1, line2Pt2);
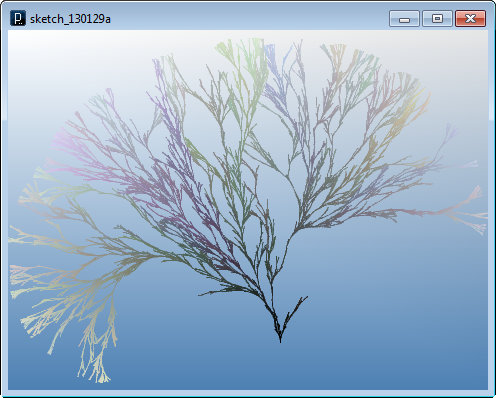
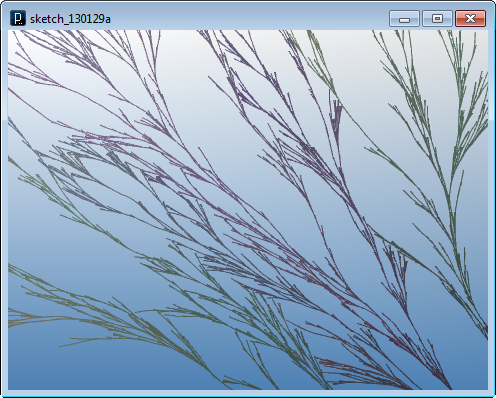
Another note is that those two intersection methods are intersection of lines in 3D space and if they are not exactly intersecting in 3D within the tolerance (defined by IConfig.tolerance), it returns a null value. If you care about intersections only on 2D, you can use intersection methods in IVec2 class. It can be slightly faster to run.
IVec2.intersectSegment(line1Pt1, line1Pt2, line2Pt1, line2Pt2);
All input arguments and a return value are instances of IVec2, not IVec. To apply this 2D intersection in the previous code, you need to convert IVec to IVec2 by to2d() method as following. To convert IVec2 to IVec, you can use to3d() method.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
add_library('igeo')
def setup() :
size(480, 360, IG.GL)
IG.duration(250)
LineAgent(IVec(0,0,0), IVec(0,1,0)).clr(0)
class LineAgent(IAgent) :
def __init__(self, pt, dir) :
self.pt1 = pt
self.pt2 = pt.cp(dir)
self.isColliding=False
def interact(self, agents) :
if self.time() == 0 : #only in the first time
for agent in agents :
if isinstance(agent, LineAgent) :
if agent is not self :
if not agent.isColliding and not self.isColliding :
intxn = IVec2.intersectSegment\
(self.pt1.to2d(), \
self.pt2.to2d(), \
agent.pt1.to2d(),\
agent.pt2.to2d())
if intxn is not None : #intersection exists
if not intxn.eq(self.pt1.to2d()) : #not parent agent
self.isColliding = True
def update(self) :
if self.isColliding :
self.del()
elif self.time() == 0 : #if not colliding
ICurve(self.pt1,self.pt2).clr(self.clr())
dir = self.pt2.dif(self.pt1)
r = self.red()+IRand.get(0,0.01)
g = self.green()+IRand.get(0,0.01)
b = self.blue()+IRand.get(0,0.01)
if IRand.pct(40) : #bend
LineAgent(self.pt2, dir.dup().rot(IRand.get(0,PI/20))).clr(r,g,b)
if IRand.pct(40) : #bend the other way
LineAgent(self.pt2, dir.dup().rot(-IRand.get(0,PI/20))).clr(r,g,b)
if IRandom.pct(40) : #straight
LineAgent(self.pt2, dir.dup()).clr(r,g,b)
 HOME
HOME
 FOR PROCESSING
FOR PROCESSING
 DOWNLOAD
DOWNLOAD
 DOCUMENTS
DOCUMENTS
 TUTORIALS (Java /
Python)
TUTORIALS (Java /
Python)
 GALLERY
GALLERY
 SOURCE CODE(GitHub)
SOURCE CODE(GitHub)
 PRIVACY POLICY
PRIVACY POLICY
 ABOUT/CONTACT
ABOUT/CONTACT
