
 Python Tutorials Python Tutorials | (back to the list of tutorials) |
 Multi-Agent 2D Example 1
Multi-Agent 2D Example 1![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
add_library('igeo')
def setup() :
size(480,360,IG.GL)
IG.duration(150)
LineAgent(IG.v(0,0,0), IG.v(1,0,0), PI/3, 20, 30, 100).clr(0.3)
LineAgent(IG.v(100,0,0), IG.v(-1,0,0), PI/2, 20, 0, 100).clr(0.3)
LineAgent(IG.v(-20,50,0), IG.v(0,-1,0), PI/2, 10, 0, 100).clr(0.3)
LineAgent(IG.v(0,-100,0), IG.v(0,1,0), PI/2, 10, 10, 100).clr(0.3)
LineAgent(IG.v(-40,0,0), IG.v(1,0,0), PI*0.4, 20, 30, 100).clr(0.3)
LineAgent(IG.v(-100,40,0), IG.v(1,1,0), PI/2, 10, 10, 100).clr(0.3)
class LineAgent(IAgent) :
length = 2
clearance = 1.99 #less than length
def __init__(self, pt, dir, ang, \
percent1, percent2, percent3 ) :
self.pt1 = pt
self.pt2 = pt.dup().add(dir.dup().len(LineAgent.length))
self.isColliding = False
self.angle = ang
self.pct1 = percent1
self.pct2 = percent2
self.pct3 = percent3
def interact(self, agents) :
if self.time() == 0 : #only in the first time
for agent in agents :
if self.isColliding :
return
if isinstance(agent, LineAgent) :
if agent is not self : #agents include "self"
# checking clearance of end point
if agent.pt2.dist(self.pt2) < LineAgent.clearance :
self.isColliding = True
def update(self ) :
if self.isColliding :
self.del()
elif self.time() == 0 : #if not colliding
ICurve(self.pt1,self.pt2).clr(self.clr())
dir = self.pt2.dif(self.pt1)
r = self.red()+IRand.get(-0.03,0.03)
g = self.green()+IRand.get(-0.03,0.03)
b = self.blue()+IRand.get(-0.03,0.03)
if IRand.pct(self.pct1) : #bend
LineAgent(self.pt2,dir.cp().rot(self.angle),\
self.angle,self.pct1,self.pct2,self.pct3).clr(r,g,b)
if IRand.pct(self.pct2) : #bend the other way
LineAgent(self.pt2,dir.cp().rot(-self.angle),\
self.angle,self.pct1,self.pct2,self.pct3).clr(r,g,b)
if IRand.pct(self.pct3) : #straight
LineAgent(self.pt2,dir.cp(),\
self.angle,self.pct1,self.pct2,self.pct3).clr(r,g,b)
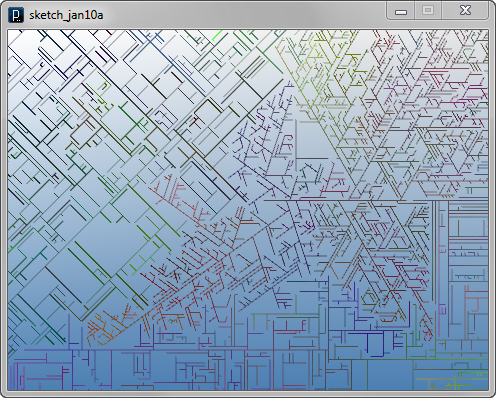
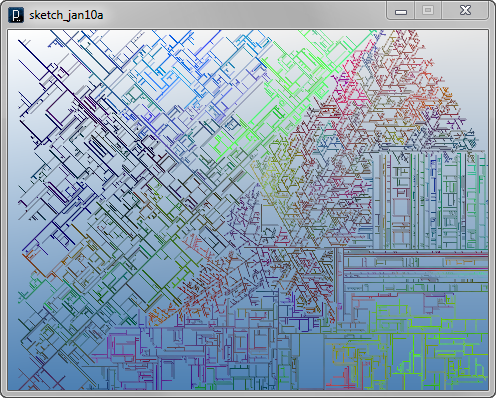
Next, blocking agents are added to exclude some lines on some location. The class of blocking agents is BlockAgent. Comparing with the previous example of blocking agents, there is a difference in the location of the code which checks the location of agents and deletes. In the previous example, location checking is done in the interact method of LineBlockAgent but in the code below, LineAgent itself check the location of blocking agent inside its interact method. In the code below, branching angle and probability are randomly defined at setup method.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
add_library('igeo')
def setup() :
size(480,360,IG.GL)
IG.duration(150)
for i in range(15) :
LineAgent(IRand.pt(300,200,0), IRand.dir(IG.zaxis),\
IRand.get(PI*0.11,PI*0.3),IRand.get(90,100),\
IRand.get(50,90),IRand.get(0,20)).clr(0)
BlockAgent(IG.v(0,0,0), 20)
BlockAgent(IG.v(-30,80,0), 30)
BlockAgent(IG.v(50,50,0), 30)
BlockAgent(IG.v(180,150,0), 50)
BlockAgent(IG.v(0,-120,0), 80)
class BlockAgent(IAgent) :
def __init__(self, p, r) :
self.pt = p
self.radius = r
def isColliding(self, agent) :
if agent.pt2.dist(self.pt) < self.radius :
return True
return False
class LineAgent(IAgent) :
length = 2
clearance = 1.99 #less than length
def __init__(self, pt, dir, ang, \
percent1,percent2,percent3) :
self.pt1 = pt
self.pt2 = pt.dup().add(dir.dup().len(LineAgent.length))
self.isColliding=False
self.angle = ang
self.pct1 = percent1
self.pct2 = percent2
self.pct3 = percent3
def interact(self, agents) :
if self.time() == 0 : #only in the first time
for agent in agents :
if self.isColliding :
return
if isinstance(agent, LineAgent) :
if agent is not self : #agents include "self"
# checking clearance of end point
if agent.pt2.dist(self.pt2) < LineAgent.clearance :
self.isColliding=True
elif isinstance(agent, BlockAgent) :
if agent.isColliding(self) :
self.isColliding=True
def update(self) :
if self.isColliding :
self.del()
elif self.time() == 0 : #if not colliding
ICurve(self.pt1,self.pt2).clr(self.clr())
dir = self.pt2.dif(self.pt1)
r = self.red()+IRand.get(-0.02,.035)
g = self.green()+IRand.get(-0.02,.035)
b = self.blue()+IRand.get(-0.02,.035)
if IRand.pct(self.pct1) : #bend
LineAgent(self.pt2,dir.cp().rot(self.angle),\
self.angle,self.pct1,self.pct2,self.pct3).clr(r,g,b)
if IRand.pct(self.pct2) : #bend the other way
LineAgent(self.pt2,dir.cp().rot(-self.angle),\
self.angle,self.pct1,self.pct2,self.pct3).clr(r,g,b)
if IRand.pct(self.pct3) : #straight
LineAgent(self.pt2,dir.cp(),self.angle,\
self.pct1,self.pct2,self.pct3).clr(r,g,b)
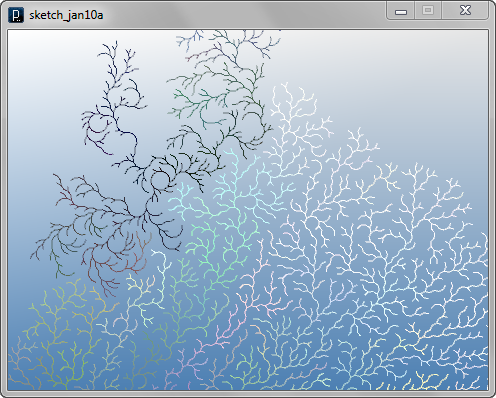
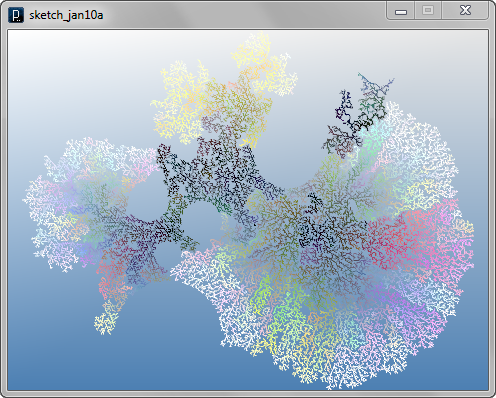
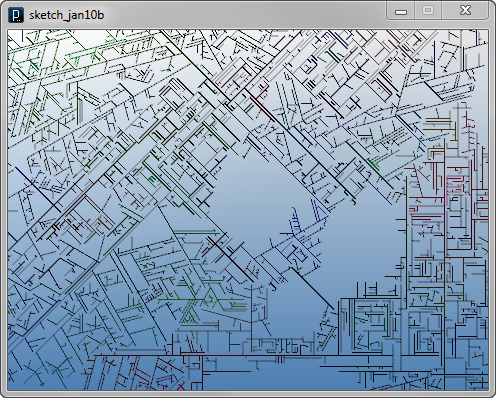
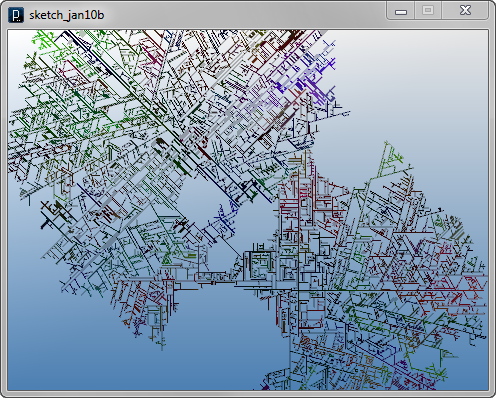
The example below changes the branching angle inside the agent itself in the middle of the propagation process. In the update method, sometimes with a certain probability, the variable angle is increased or decreased stochastically. There is another stochastic feature added for the blocking agent. The line agent sometimes ignores the blocking agent and keep propagating inside the blocking area by if-condition in the interact method of LineAgent
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
add_library('igeo')
def setup() :
size(480,360,IG.GL)
IG.duration(150)
LineAgent(IG.v(100,-50,0), IG.v(0,1,0), PI/2, 20,10,99).clr(0)
LineAgent(IG.v(-50,150,0), IG.v(1,1,0), PI/2, 20,10,99).clr(0)
BlockAgent(IG.v(0,0,0), 20)
BlockAgent(IG.v(-30,80,0), 30)
BlockAgent(IG.v(50,50,0), 30)
BlockAgent(IG.v(180,150,0), 50)
BlockAgent(IG.v(0,-120,0), 80)
class BlockAgent(IAgent) :
def __init__(self, p, r) :
self.pt = p
self.radius = r
def isColliding(self, agent) :
if agent.pt2.dist(self.pt) < self.radius :
return True
return False
class LineAgent(IAgent) :
length = 2
clearance = 1.99 #less than length
def __init__(self, pt, dir, ang, \
percent1,percent2,percent3) :
self.pt1 = pt
self.pt2 = pt.dup().add(dir.dup().len(LineAgent.length))
self.isColliding=False
self.angle = ang
self.pct1 = percent1
self.pct2 = percent2
self.pct3 = percent3
def interact(self, agents) :
if self.time() == 0 : #only in the first time
for agent in agents :
if self.isColliding :
return
if isinstance(agent, LineAgent) :
if agent is not self : #agents include "this"
# checking clearance of end point
if agent.pt2.dist(self.pt2) < LineAgent.clearance :
self.isColliding=True
elif isinstance(agent, BlockAgent) :
if agent.isColliding(self) :
if IRand.pct(80) : #ignores block agent in 20%
self.isColliding=True
def update(self) :
if self.isColliding :
self.del()
elif self.time() == 0 : #if not colliding
ICurve(self.pt1,self.pt2).clr(self.clr())
dir = self.pt2.dif(self.pt1)
if IRand.pct(2) : #change angle occasionally
if IRand.pct(50) :
self.angle+=PI/12
else :
self.angle -= PI/12
r = self.red()+IRand.get(-0.03,0.03)
g = self.green()+IRand.get(-0.03,0.03)
b = self.blue()+IRand.get(-0.03,0.03)
if IRand.pct(self.pct1) : #bend
LineAgent(self.pt2,dir.cp().rot(self.angle),\
self.angle,self.pct1,self.pct2,self.pct3).clr(r,g,b)
if IRand.pct(self.pct2) : #bend the other way
LineAgent(self.pt2,dir.cp().rot(-self.angle),\
self.angle,self.pct1,self.pct2,self.pct3).clr(r,g,b)
if IRand.pct(self.pct3) : #straight
LineAgent(self.pt2,dir.cp(),\
self.angle,self.pct1,self.pct2,self.pct3).clr(r,g,b)
 HOME
HOME
 FOR PROCESSING
FOR PROCESSING
 DOWNLOAD
DOWNLOAD
 DOCUMENTS
DOCUMENTS
 TUTORIALS (Java /
Python)
TUTORIALS (Java /
Python)
 GALLERY
GALLERY
 SOURCE CODE(GitHub)
SOURCE CODE(GitHub)
 PRIVACY POLICY
PRIVACY POLICY
 ABOUT/CONTACT
ABOUT/CONTACT
