
 Python Tutorials Python Tutorials | (back to the list of tutorials) |
 Multi-Agent 2D Example 2 (requires iGeo version 7.5.1 or higher)
Multi-Agent 2D Example 2 (requires iGeo version 7.5.1 or higher)IVec.intersectLine(pt1,pt2,a.pt1,a.pt2)!=null
The input argument of the intersectLine() method is 4 vector varaibles of one end point of the first line, another end point of the first line, one end point of the second line, and another end point of the second line. It returns an intersection point of two line as IVec variable but if they don't intersect, it returns null value. The two more conditions !pt1.eq(a.pt1) and !pt1.eq(a.pt2) inside the if-condition statement exclude the case of the parent line agent or other branching line agents which share the same parent agent.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
add_library('igeo')
def setup() :
size(480, 360, IG.GL)
IG.duration(300)
LineAgent(IVec(0,0,0), IVec(0,1,0)).clr(0)
class LineAgent(IAgent) :
def __init__(self, pt, dir) :
self.pt1 = pt
self.pt2 = pt.cp(dir)
self.isColliding = False
def interact(self, agents) :
if self.time() == 0 : #only in the first time
for agent in agents :
if self.isColliding :
return
if isinstance(agent, LineAgent) :
# checking clearance of end point
if not self.pt1.eq(agent.pt1) and \
not self.pt1.eq(agent.pt2) and \
IVec.intersectLine(self.pt1,self.pt2,agent.pt1,agent.pt2)is not None :
self.isColliding=True
def update(self) :
if self.isColliding :
self.del()
elif self.time() == 0 : #if not colliding
ICurve(self.pt1,self.pt2).clr(self.clr())
dir = self.pt2.dif(self.pt1)
r = self.red() + IRand.get(-0.06,0.06)
g = self.green() + IRand.get(-0.06,0.06)
b = self.blue() + IRand.get(-0.06,0.06)
if IRand.pct(2.5) : #branching
num = 15
for i in range(1, num) :
if IRand.pct(40) :
dir2 = dir.dup().rev()
dir2.rot(2*PI*i/num)
LineAgent(self.pt2,dir2).clr(r,g,b)
elif IRand.pct(99) : #going straight
LineAgent(self.pt2,dir).clr(r,g,b)

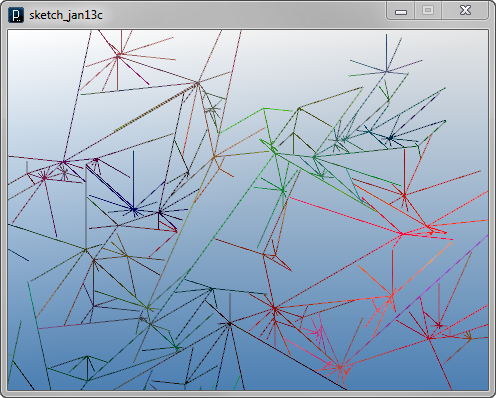
The next code adds just one line to let the agent turn slightly instead of going straight by rotating the direction vector dir.
dir.rot( PI/80 );
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
add_library('igeo')
def setup() :
size(480, 360, IG.GL)
IG.duration(300)
LineAgent(IVec(0,0,0), IVec(0,1,0)).clr(0)
class LineAgent(IAgent) :
def __init__(self, pt, dir) :
self.pt1 = pt
self.pt2 = pt.cp(dir)
self.isColliding = False
def interact(self, agents) :
if self.time() == 0 : #only in the first time
for agent in agents :
if self.isColliding :
return
if isinstance(agent, LineAgent) :
# checking clearance of end point
if not self.pt1.eq(agent.pt1) and \
not self.pt1.eq(agent.pt2) and \
IVec.intersectLine(self.pt1,self.pt2,agent.pt1,agent.pt2)is not None :
self.isColliding=True
def update(self) :
if self.isColliding :
self.del()
elif self.time() == 0 : #if not colliding
ICurve(self.pt1,self.pt2).clr(self.clr())
dir = self.pt2.dif(self.pt1)
r = self.red() + IRand.get(-0.06,0.06)
g = self.green() + IRand.get(-0.06,0.06)
b = self.blue() + IRand.get(-0.06,0.06)
if IRand.pct(2.5) : #branching
num = 15
for i in range(1, num) :
if IRand.pct(40) :
dir2 = dir.dup().rev()
dir2.rot(2*PI*i/num)
LineAgent(self.pt2,dir2).clr(r,g,b)
elif IRand.pct(99) : #going straight
dir.rot(PI/80)
LineAgent(self.pt2,dir).clr(r,g,b)
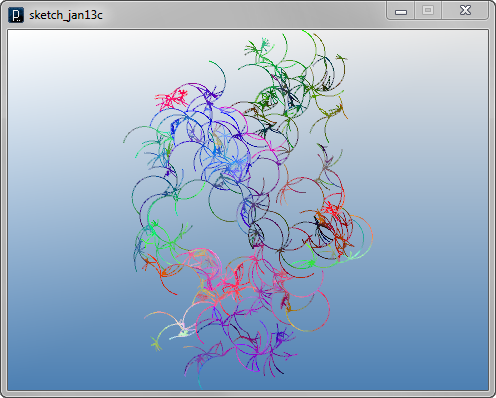
The code below randomize the move of an agent when it doesn't create branches by randomly rotating the direction vector dir.
dir.rot( IRand.get(-PI/8, PI/8) );
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
add_library('igeo')
def setup() :
size(480, 360, IG.GL)
IG.duration(300)
LineAgent(IVec(0,0,0), IVec(0,1,0)).clr(0)
class LineAgent(IAgent) :
def __init__(self, pt, dir) :
self.pt1 = pt
self.pt2 = pt.cp(dir)
self.isColliding = False
def interact(self, agents) :
if self.time() == 0 : #only in the first time
for agent in agents :
if self.isColliding :
return
if isinstance(agent, LineAgent) :
# checking clearance of end point
if not self.pt1.eq(agent.pt1) and \
not self.pt1.eq(agent.pt2) and \
IVec.intersectLine(self.pt1,self.pt2,agent.pt1,agent.pt2)is not None :
self.isColliding=True
def update(self) :
if self.isColliding :
self.del()
elif self.time() == 0 : #if not colliding
ICurve(self.pt1,self.pt2).clr(self.clr())
dir = self.pt2.dif(self.pt1)
r = self.red() + IRand.get(-0.06,0.06)
g = self.green() + IRand.get(-0.06,0.06)
b = self.blue() + IRand.get(-0.06,0.06)
if IRand.pct(2.5) : #branching
num = 15
for i in range(1, num) :
if IRand.pct(40) :
dir2 = dir.dup().rev()
dir2.rot(2*PI*i/num)
LineAgent(self.pt2,dir2).clr(r,g,b)
elif IRand.pct(99) : #going straight
dir.rot(IRand.get(-PI/20,PI/20))
LineAgent(self.pt2,dir).clr(r,g,b)


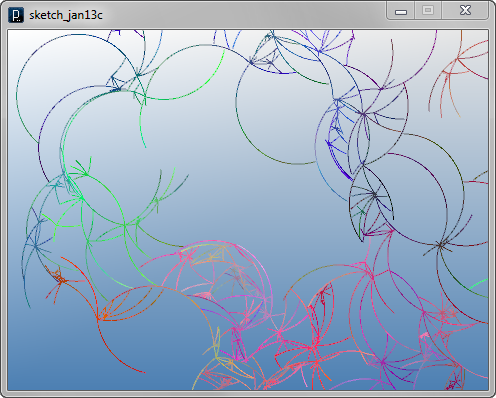
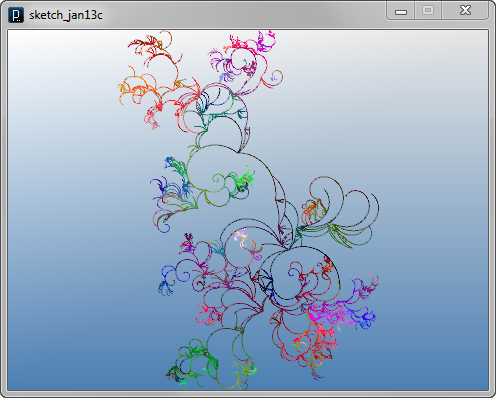
This code below changes two parts of
the second rotating agent code.
First, the range of branching angle is limited to
Pi, instead of 2 Pi, by changing this line in the previous code
dir2.rot( 2*PI*i/num );
to
dir2.rot( PI*i/num );
The second change is to scale down (or sometimes up)
the length of
line agents in both cases of creating branch agents and just going
with a single agent.
This is done by multiplying some number to the
direction vector dir for a single agent
or dir2 for branching
agents in those lines.
dir2.mul( IRand.get(0.9, 1.35) ); //scale up or down
dir.mul( 0.98 ); //scale down
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
add_library('igeo')
def setup() :
size(480, 360, IG.GL)
IG.duration(250)
LineAgent(IVec(0,0,0), IVec(0,1,0)).clr(0)
class LineAgent(IAgent) :
def __init__(self, pt, dir) :
self.pt1 = pt
self.pt2 = pt.cp(dir)
self.isColliding = False
def interact(self, agents) :
if self.time() == 0 : #only in the first time
for agent in agents :
if self.isColliding :
return
if isinstance(agent, LineAgent) :
# checking clearance of end point
if not self.pt1.eq(agent.pt1) and \
not self.pt1.eq(agent.pt2) and \
IVec.intersectLine(self.pt1,self.pt2,agent.pt1,agent.pt2)is not None :
self.isColliding=True
def update(self) :
if self.isColliding :
self.del()
elif self.time() == 0 : #if not colliding
ICurve(self.pt1,self.pt2).clr(self.clr())
dir = self.pt2.dif(self.pt1)
r = self.red() + IRand.get(-0.06,0.06)
g = self.green() + IRand.get(-0.06,0.06)
b = self.blue() + IRand.get(-0.06,0.06)
if IRand.pct(2.5) : #branching
num = 15
for i in range(1, num) :
if IRand.pct(40) :
dir2 = dir.dup().rev()
dir2.rot(PI*i/num);
dir2.mul(IRand.get(0.9, 1.35)) #scale up or down
LineAgent(self.pt2,dir2).clr(r,g,b)
elif IRand.pct(99) : #going straight
dir.rot(PI/40);
dir.mul(0.98); #scale down
LineAgent(self.pt2,dir).clr(r,g,b)

 HOME
HOME
 FOR PROCESSING
FOR PROCESSING
 DOWNLOAD
DOWNLOAD
 DOCUMENTS
DOCUMENTS
 TUTORIALS (Java /
Python)
TUTORIALS (Java /
Python)
 GALLERY
GALLERY
 SOURCE CODE(GitHub)
SOURCE CODE(GitHub)
 PRIVACY POLICY
PRIVACY POLICY
 ABOUT/CONTACT
ABOUT/CONTACT
