
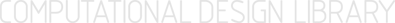
 Tutorials Tutorials | (back to the list of tutorials) |
 Creating Curves with Arrays
Creating Curves with Arrays
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
import processing.opengl.*;
import igeo.*;
size( 480, 360, IG.GL );
IVec[] cpts1 = new IVec[4];
cpts1[0] = new IVec(-30, 10, 0);
cpts1[1] = new IVec(-10, 10, 0);
cpts1[2] = new IVec(-10, 30, 0);
cpts1[3] = new IVec(-30, 30, 0);
// curve 1 (red)
new ICurve(cpts1, 3).clr(1.,0,0);
IVec[] cpts2 = new IVec[10];
for(int i=0; i < cpts2.length; i++){
if(i%2==0){ cpts2[i] = new IVec(i*10, 0, 0); }
else{ cpts2[i] = new IVec(i*10, 10, 0); }
}
// curve 2 (blue)
new ICurve(cpts2, 1).clr(0,0,1.);
IVec[] cpts3 = new IVec[16];
for(int i=0; i < cpts3.length; i++){
if(i%4==0){ cpts3[i] = new IVec(-30, -10, i*5); }
else if(i%4==1){ cpts3[i] = new IVec(-10, -10, i*5); }
else if(i%4==2){ cpts3[i] = new IVec(-10, -30, i*5); }
else{ cpts3[i] = new IVec(-30, -30, i*5); } // same with i%4==3
}
// curve 3 (cyan)
new ICurve(cpts3, 3).clr(0,1.,1.);
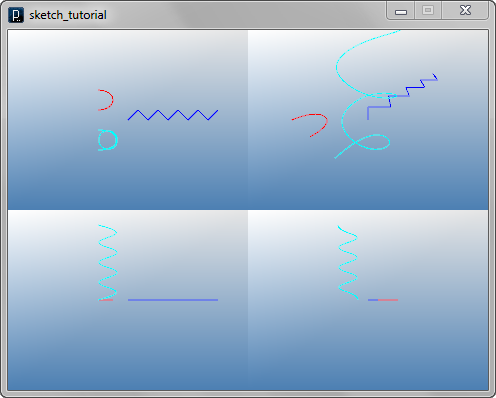
 Creating Surfaces with Arrays
Creating Surfaces with Arrays
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
import processing.opengl.*;
import igeo.*;
size( 480, 360, IG.GL );
IVec[][] cpts1 = new IVec[2][2];
cpts1[0][0] = new IVec( 0, 0, 0);
cpts1[1][0] = new IVec(-30, 0, 0);
cpts1[0][1] = new IVec( 0,-30, 0);
cpts1[1][1] = new IVec(-30,-30, 0);
// surface 1 (gray)
new ISurface(cpts1);
IVec[][] cpts2 = new IVec[10][2];
for(int i=0; i < cpts2.length; i++){
if(i%2==0){
cpts2[i][0] = new IVec(i*10,0,0);
cpts2[i][1] = new IVec(i*10,0,20);
}
else{
cpts2[i][0] = new IVec(i*10,-10,0);
cpts2[i][1] = new IVec(i*10,10,10);
}
}
// surface 2 (purple)
new ISurface(cpts2).clr(.5,0,1);
IVec[][] cpts3 = new IVec[4][4];
for(int i=0; i < cpts3.length; i++){
for(int j=0; j < cpts3[i].length; j++){
if( (i==0||i==3) && (j==1||j==2) ){
cpts3[i][j] = new IVec(-i*10, j*10, 20);
}
else{ cpts3[i][j] = new IVec(-i*10, j*10, 0); }
}
}
// surface 3 (pink)
new ISurface(cpts3,3,3).clr(1,.5,1);
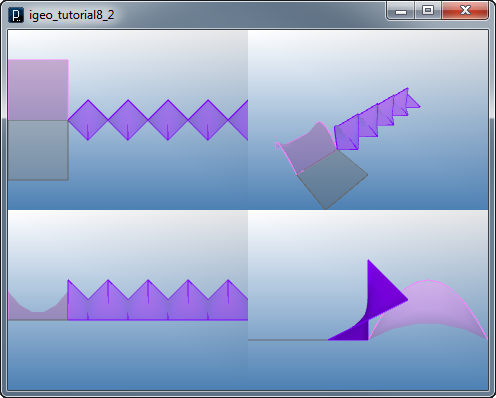
 Creating Polygon Mesh with Arrays
Creating Polygon Mesh with Arrays
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
import processing.opengl.*;
import igeo.*;
size( 480, 360, IG.GL );
IVec[][] cpts1 = new IVec[10][10];
for(int i=0; i < cpts1.length; i++){
for(int j=0; j < cpts1[i].length; j++){
if( (i+j)%2==0 ){
cpts1[i][j] = new IVec(i*5, -j*5-30, (i+j)*2);
}
else{ cpts1[i][j] = new IVec(i*5, -j*5-30, (i+j-1)*2); }
}
}
// mesh 1 (cyan)
new IMesh(cpts1).clr(0,1.,1.);
int divNum=30;
IVec[][] cpts2 = new IVec[10][divNum+1];
for(int i=0; i < cpts2.length; i++){
for(int j=0; j < cpts2[i].length; j++){
float radius = 30 - i*3;
float angle = 2 * PI / divNum * j;
cpts2[i][j] =
new IVec(cos(angle)*radius, sin(angle)*radius, i*i*.5);
}
}
// mesh 2 (red)
new IMesh(cpts2).clr(1.,0,0);
Note that the use of constant PI to calculate the angle to be used in
trigonometric function. divNum is dividing 2 * PI,
not 360 because the unit of sin() and cos() is not degree
but radian.
Please also note that the length of the array cpts2 in the
second dimension is not divNum but divNum+1
to match points on the end edge with points on the start edge.
 HOME
HOME
 FOR PROCESSING
FOR PROCESSING
 DOWNLOAD
DOWNLOAD
 DOCUMENTS
DOCUMENTS
 TUTORIALS (Java /
Python)
TUTORIALS (Java /
Python)
 GALLERY
GALLERY
 SOURCE CODE(GitHub)
SOURCE CODE(GitHub)
 PRIVACY POLICY
PRIVACY POLICY
 ABOUT/CONTACT
ABOUT/CONTACT
